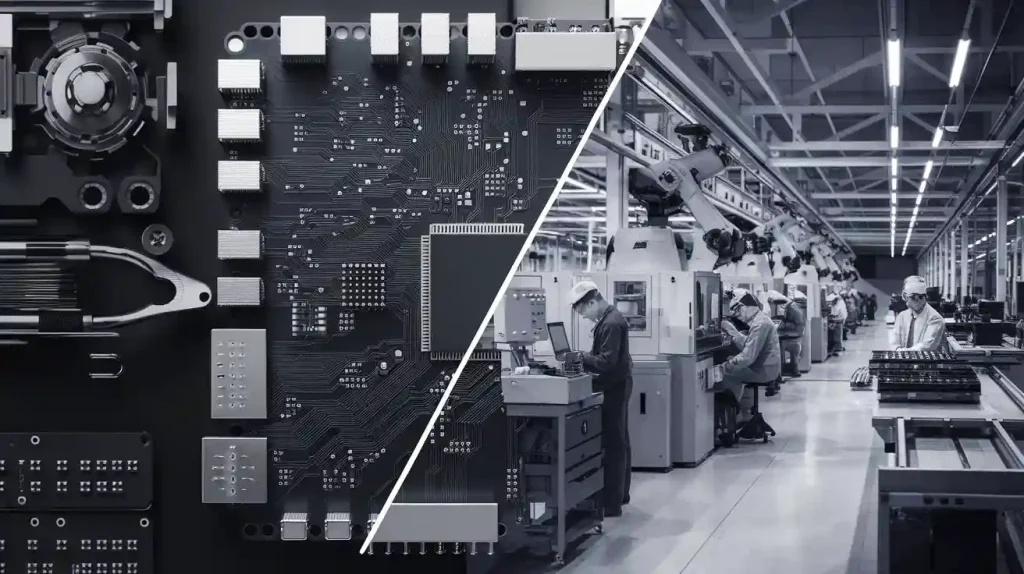
PCB Board House vs Factory: Key Differences
When choosing a partner for printed circuit board (PCB) production, understanding the capabilities of different providers is essential. A PCB board house typically excels in small-scale projects, offering design services and customisation for prototypes. This flexibility suits industries requiring unique solutions. However, PCB factories dominate large-scale manufacturing. Their focus on automation and efficiency ensures consistent quality and cost-effectiveness. For instance, China, leading in PCB production, leverages advanced laser-based cutting systems, which improve accuracy by 30% and reduce defects. Such innovations make factories the preferred choice for mass production, especially in sectors demanding precision and scalability.
Key Takeaways
- PCB board houses are great for custom designs and small jobs.
- PCB factories are built for making many boards at lower costs.
- Factories deliver faster because they use machines and quick methods.
- Think about your project needs; pick a board house for detailed work or a factory for big orders and savings.
- Some options mix both, giving custom designs and large production together.
Definition and Role
What is a PCB Board House?
A PCB board house serves as a specialised facility for designing and prototyping printed circuit boards. It caters to projects requiring small-scale production and high levels of customisation. You can rely on a board house for services like schematic design, layout optimisation, and prototype fabrication. These facilities often work closely with engineers and designers to refine concepts before moving to mass production.
Board houses excel in flexibility. They adapt to unique project requirements, whether you need a single-layer PCB or a complex multi-layer design. Their focus on precision and detail makes them ideal for industries like aerospace, medical devices, and research and development. However, their limited production capacity may not suit large-scale manufacturing needs.
Key factors to consider when evaluating a PCB board house include its technical capabilities, certifications, and communication efficiency. For instance, certifications like ISO 9001 ensure adherence to quality standards, while effective communication helps address technical queries promptly. The table below summarises these considerations:
| Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Capabilities | PCB manufacturers must evaluate their technical capabilities, including equipment and technology to meet project specifications. |
| Certifications | Quality certifications like ISO 9001 and AS9100 indicate the level of quality management and compliance with industry standards. |
| Production Capacity | The ability to meet production demands and turnaround times is crucial for project success. |
| Communication | Effective communication during the manufacturing process is essential for ensuring project success and addressing technical questions. |
| Geographical Location | The choice between domestic and overseas manufacturers affects logistics, turnaround times, and communication. |
What is a PCB Factory?
A PCB factory is a large-scale facility dedicated to high-volume PCB manufacturing. These factories prioritise efficiency, automation, and scalability to meet the demands of industries like consumer electronics, automotive, and telecommunications. Unlike a PCB board house, a factory focuses on mass production, ensuring consistent quality and cost-effectiveness.
Factories leverage advanced technologies to optimise production processes. For example, a case study from a consumer electronics manufacturer revealed significant improvements in efficiency. Production capacity increased from 10,000 to 85,000 units per day, while defect rates dropped from 2% to 0.02%. Such advancements highlight the factory’s ability to deliver high-quality products at scale.
Additionally, PCB factories often comply with stringent industry standards, such as ISO/TS 16949 for automotive electronics or FDA requirements for medical devices. These certifications ensure reliability and regulatory compliance, making factories the preferred choice for large-scale projects. Their ability to handle diverse product variants and maintain zero-defect manufacturing further underscores their suitability for mass production.
| Case Study | Key Improvements |
|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics Manufacturer | Production capacity increased from 10,000 to 85,000 units per day, defect rates decreased from 2% to 0.02%, time-to-market reduced by 65%, labour costs reduced by 78%, energy consumption decreased by 42%. |
| Automotive Electronics Supplier | Production flexibility for 230+ product variants, first-pass yield improved from 92% to 99.7%, warranty claims reduced by 83%, space utilisation improved by 45%, ISO/TS 16949 compliance achieved. |
| Medical Device Startup | Achieved FDA compliance, reduced validation time by 70%, maintained zero-defect manufacturing, scaled production from 100 to 5,000 units monthly, reduced time-to-market from 18 months to 7 months. |
Key Differences
Services Offered
When comparing a PCB board house and a PCB factory, the range of services provided is a critical distinction. A PCB board house typically focuses on design, prototyping, and small-scale PCB fabrication. You can expect services such as schematic design, layout optimisation, and prototype testing. These facilities often work closely with engineers to refine concepts, making them ideal for projects in the early stages of development.
In contrast, a PCB factory offers end-to-end solutions for large-scale PCB manufacturing. Factories handle everything from raw material procurement to final PCB assembly. Advanced automation and streamlined processes allow factories to produce high volumes while maintaining consistent quality. Many factories also provide value-added services like component sourcing, surface-mount technology (SMT) assembly, and thorough quality control measures. These capabilities make factories better suited for industries requiring mass production, such as automotive and consumer electronics.
Scale of Operations
The scale of operations is another area where the two differ significantly. A PCB board house operates on a smaller scale, catering to low-volume orders and niche requirements. This limited capacity allows for greater attention to detail but restricts the ability to meet high-volume demands. If your project involves only a few units or experimental designs, a board house might suffice.
On the other hand, a PCB factory is built for high-volume production. These facilities can manufacture thousands—or even millions—of printed circuit boards in a single production run. Factories leverage advanced machinery and optimised workflows to achieve economies of scale. This efficiency not only reduces costs but also ensures faster turnaround times for bulk orders. For large-scale projects, a factory’s capacity and scalability are unmatched.
Customisation and Flexibility
Customisation is where a PCB board house truly shines. These facilities excel at tailoring designs to meet specific requirements. Whether you need a unique multi-layer PCB or a specialised material, a board house can accommodate your needs. Their flexibility makes them a popular choice for industries like aerospace and medical devices, where bespoke solutions are often necessary.
However, this level of customisation comes at a cost. Board houses may struggle to maintain consistency and efficiency when scaling up production. In contrast, a PCB factory prioritises standardisation. While factories can offer some degree of customisation, their primary focus is on producing standardised designs at scale. This approach ensures uniform quality across large batches, making factories the preferred option for projects where consistency and cost-effectiveness are paramount.
Tip: If your project requires both customisation and scalability, consider working with a PCB manufacturer that offers hybrid solutions. Some factories now integrate design and prototyping services, bridging the gap between flexibility and mass production.
Cost Implications
Cost plays a pivotal role in deciding between a PCB board house and a PCB factory. If your project involves small-scale PCB fabrication, a board house may seem appealing due to its focus on prototyping and design services. However, this option often comes with higher per-unit costs. The limited production capacity and manual processes in board houses contribute to increased expenses. For instance, customisation and prototype testing require specialised attention, which drives up costs further.
On the other hand, PCB factories excel in cost efficiency, especially for large-scale PCB manufacturing. Factories leverage economies of scale to reduce production costs significantly. Automated workflows and bulk material procurement minimise overheads, making factories the preferred choice for high-volume orders. For example, a factory can produce thousands of printed circuit boards at a fraction of the cost per unit compared to a board house. Additionally, factories often include value-added services like PCB assembly and quality control measures within their pricing structure, further enhancing cost-effectiveness.
Note: While board houses may suit niche projects requiring intricate designs, factories offer unmatched affordability for mass production. If your goal is to optimise costs without compromising quality, a PCB factory is the ideal solution.
Turnaround Time
Turnaround time is another critical factor to consider when choosing between a PCB board house and a factory. Board houses typically operate on smaller scales, which allows them to focus on detailed prototyping and design refinement. However, this attention to detail often results in longer lead times. If your project demands rapid delivery, a board house may struggle to meet tight deadlines.
PCB factories, in contrast, are designed for speed and efficiency. Advanced machinery and streamlined processes enable factories to complete large-scale PCB manufacturing in record time. For example, automated PCB assembly lines can produce thousands of units daily, ensuring faster delivery for bulk orders. Factories also maintain robust supply chains, which minimise delays in material procurement and production. This efficiency makes factories the preferred choice for industries requiring quick turnaround times, such as consumer electronics and automotive sectors.
Tip: If your project timeline is critical, prioritise a PCB factory. Their ability to handle high-volume production with minimal delays ensures your printed circuit boards are ready when you need them.
Choosing the Right Option
When to Choose a PCB Board House
A PCB board house is ideal for projects requiring high levels of customisation and small-scale production. If your design involves intricate features or experimental layouts, a board house can provide the flexibility needed to refine your concept. These facilities specialise in prototyping, making them suitable for industries like medical devices and aerospace, where precision and innovation are critical.
For example, the ASC Sunstone case study highlights the importance of early collaboration with PCB fabricators during the design phase. This approach ensures that prototypes meet stringent requirements, reducing the risk of costly revisions later. Similarly, reverse engineering LED PCBs has demonstrated significant benefits, such as a 22% reduction in BOM costs and improved energy efficiency from 110 lm/W to 135 lm/W. These metrics underscore the value of working with a board house for projects prioritising customisation over scalability.
However, board houses often struggle with large-scale production due to limited capacity and higher per-unit costs. If your project demands rapid delivery or bulk manufacturing, a PCB board house may not be the most efficient choice.
When to Choose a PCB Factory
A PCB factory is the optimal choice for large-scale manufacturing and projects requiring consistent quality. Factories leverage advanced automation and streamlined workflows to produce thousands of units efficiently. This scalability makes them ideal for industries like consumer electronics and automotive, where high-volume production is essential.
Factories also excel in cost-effectiveness. By utilising economies of scale, they significantly reduce per-unit costs. For instance, LED PCB reverse engineering has shown how factories can extend product lifespans from 50,000 to 80,000 hours while lowering maintenance costs by 35%. These benefits make factories the preferred option for projects prioritising affordability and reliability.
Additionally, factories maintain robust quality control measures, ensuring uniformity across large batches. Their ability to meet stringent industry standards, such as ISO/TS 16949 for automotive electronics, further enhances their appeal. If your project requires quick turnaround times, a factory’s automated processes and efficient supply chains ensure timely delivery without compromising quality.
Tip: For projects requiring both customisation and scalability, consider hybrid solutions offered by some PCB manufacturers. These facilities combine the flexibility of a board house with the efficiency of a factory, bridging the gap between prototyping and mass production.
Understanding the differences between a PCB board house and a PCB factory is crucial for making the right choice. A board house offers flexibility and customisation, making it suitable for small-scale projects or prototypes. However, its limited capacity and higher costs can hinder large-scale production. A PCB factory, on the other hand, excels in mass manufacturing. Its advanced automation ensures consistent quality, cost efficiency, and faster delivery.
You should choose a PCB factory if your project demands high-volume production, affordability, and reliability. Factories provide the scalability and efficiency needed for industries like automotive and consumer electronics. For most manufacturing needs, a factory remains the optimal choice.
FAQ
What is the main difference between a PCB board house and a PCB factory?
A PCB board house focuses on small-scale production and prototyping, offering customisation. A PCB factory specialises in large-scale manufacturing, ensuring efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and consistent quality. Factories are better suited for high-volume projects requiring scalability.
Can a PCB board house handle large-scale production?
No, PCB board houses lack the capacity and infrastructure for large-scale production. Their focus remains on prototyping and low-volume orders. For bulk manufacturing, a PCB factory provides the necessary scalability and automation.
Are PCB workshop more cost-effective than board houses?
Yes, PCB factories achieve cost efficiency through economies of scale and automation. They reduce per-unit costs significantly, making them ideal for high-volume production. Board houses, with their manual processes, often incur higher costs per unit.
Do PCB shops offer customisation?
PCB factories provide limited customisation compared to board houses. However, some factories now integrate design and prototyping services, offering hybrid solutions. These options balance customisation with the efficiency of mass production.
Which option ensures faster turnaround times?
PCB factories deliver faster turnaround times due to advanced machinery and streamlined workflows. Board houses, focusing on detailed prototyping, often require longer lead times. For time-sensitive projects, factories are the better choice.
Tip: Always evaluate your project’s scale, budget, and timeline before deciding between a PCB board house and a factory.