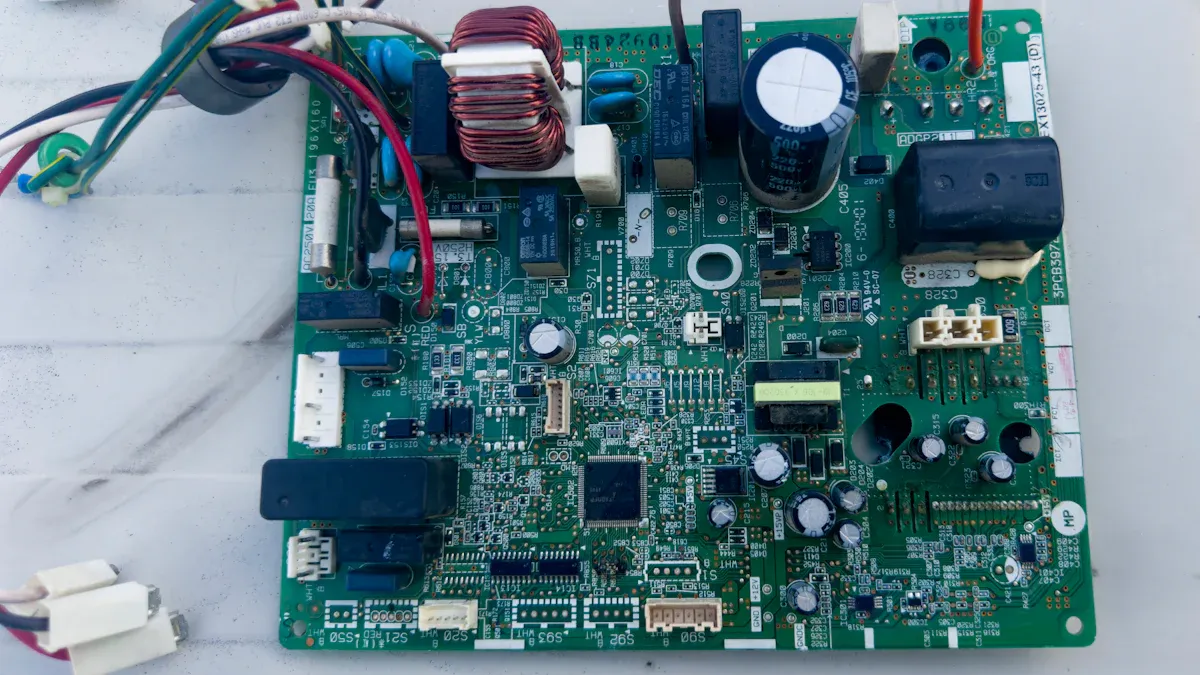
EMS PCB and PCB Testing Key Differences Explained
In making electronics, EMS PCB is key for building circuit boards. PCB testing checks if these boards work well and are high quality. Together, they help make dependable electronics.
- The worldwide Electronic Manufacturing Services market was $550.2 billion in 2022. It is expected to grow to $800 billion by 2032, with a 7.2% yearly growth rate.
- New electronics ideas increase the need for better PCB designs. Big companies (OEMs) strongly affect this market.
By learning these steps, you can make better products faster.
Key Takeaways
- EMS PCB is about building and putting together circuit boards.
- PCB testing makes sure the boards work well and are safe.
- It finds issues early to avoid bigger problems later.
- Using modern tools in EMS PCB and testing makes work faster.
- Teamwork between EMS PCB and testing teams creates better products.
- Knowing what EMS PCB and testing do helps make good electronics.
What Is EMS PCB?
Definition and Overview of EMS PCB
Electronic Manufacturing Services (EMS) PCB means making and assembling circuit boards. These services make sure PCBs work well and meet industry rules. EMS PCB follows strict guidelines, like those from IPC standards.
| IPC Standard | What It Covers |
|---|---|
| IPC-2581 | Shares design data between PCB makers and designers for better results. |
| IPC-2221 | General rules for PCB design, including layout and materials. |
| IPC-4101C | Lists rules for materials used in rigid or layered boards. |
| IPC-6012B | Sets rules for strong and solderable rigid PCBs. |
| IPC-A-600F | Explains what is acceptable or not for PCB parts. |
These rules help EMS PCB production stay reliable and high-quality.
Role of EMS in Electronics Manufacturing
EMS is very important in making electronics. It improves processes and product quality. Services include:
- Design Help: EMS providers improve designs for easier manufacturing.
- Making and Assembling: They manage production for accurate and good results.
- Flexibility: EMS adjusts production sizes based on demand.
- Saving Money: Providers cut costs with better workflows and bulk production.
- Testing: Careful testing ensures products meet industry rules.
- Supply Chain: EMS handles materials and delivery for smooth operations.
These services help businesses make affordable and dependable electronics.
Key Processes in EMS PCB Production
EMS PCB production has many steps to ensure quality and speed. Special tools and methods improve each step:
| Step | What It Does | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation Tools | Plans production using live data. | Boosts productivity and efficiency. |
| Data Collection | Tracks production and stock levels. | Avoids extra inventory. |
| Optimization | Quickly changes production lines. | Saves time and uses resources well. |
Each PCB gets a unique code, like a barcode, for tracking. Data updates at every step to find problems fast. These steps keep EMS PCB production efficient and ready for changes.
Tools and Technologies in EMS PCB
Modern tools are very important in EMS PCB making. They make work faster, improve quality, and save time. Using advanced tools helps meet the needs of electronics today.
Here are some cool tools changing EMS PCB production:
- Flex Ltd.’s Sketch-to-Scale® Solution: This tool speeds up product creation. A top phone company made products 30% faster and improved results by 15% with it.
- Jabil’s Additive Manufacturing Network: This tool makes custom items quickly. A medical company made surgical guides 60% faster than old ways.
These tools show how new tech can help you stay ahead. They make work better and ensure great results. By using these tools, EMS PCB makers can handle changes and create top products quickly.
What Is PCB Testing?
Definition and Purpose of PCB Testing
PCB testing checks if circuit boards work well and are reliable. It finds problems, tests performance, and ensures boards follow industry rules. Testing methods include simple checks like looking at the board and advanced ones like X-rays or heat tests. These steps catch issues early, saving time and money during production.
PCB testing has many uses:
- Quality Assurance: Makes sure boards match design plans.
- Defect Detection: Finds mistakes like bad soldering or broken circuits.
- Performance Validation: Tests if boards work in real-life conditions.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures boards meet safety rules like IPC and ISO.
Good testing helps you make products that work well and satisfy customers.
Importance of PCB Testing in Quality Assurance
Testing is key to keeping products high-quality. It removes problems that could cause failures later. For example, heat tests check if boards survive soldering without damage. Peel tests measure how strong copper lines stick to the board. Life tests simulate tough conditions to predict how long boards will last.
In fields like healthcare and aerospace, testing ensures boards meet strict rules. This prevents legal trouble and builds customer trust. Testing also makes products last longer and lowers repair costs. For instance, military systems became 50% more reliable with testing. A phone company cut failure rates by 30% using heat-aging tests.
Common PCB Testing Methods
PCB testing uses different ways to check quality and reliability. Each method focuses on specific board features:
- Visual Inspection: Spots visible problems like bad soldering.
- Electrical Testing: Checks circuits with in-circuit and functional tests.
- Flying Probe Testing: Uses automated probes for prototypes without special tools.
- X-Ray Inspection: Finds hidden issues inside the board.
- Thermal Stress Testing: Tests how boards handle temperature changes.
- Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): Finds assembly mistakes like cracked joints.
- Continuity Test: Checks for broken or short circuits in bare boards.
Advanced tests like Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) measure signal strength, while UL Safety Tests ensure basic reliability. Using these methods together gives strong quality control and dependable electronics.
Tools and Equipment for PCB Testing
PCB testing uses special tools to check board quality and performance. These tools find problems, test how boards work, and ensure they follow rules. Here are some important tools for PCB testing:
- Multimeters: These tools measure voltage, current, and resistance. They help find short circuits, open circuits, or other electrical problems.
- Oscilloscopes: Oscilloscopes show electrical signals as waveforms. They help spot signal issues and check how circuits behave.
- Flying Probe Testers: These machines test prototypes without needing custom setups. They use probes to check connections and find faults.
- Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) Systems: AOI systems use cameras to find defects like bad soldering or missing parts.
- X-Ray Inspection Machines: X-ray machines look inside boards to find hidden problems, like gaps in solder joints or misaligned layers.
- Thermal Imaging Cameras: These cameras show heat patterns on boards. They help find overheating parts or areas with bad heat control.
- Time Domain Reflectometers (TDR): TDR tools check signal reflections. They find issues with transmission lines and mismatched impedance.
Pro Tip: Pick tools that fit your testing needs. For example, use AOI for large batches and flying probes for prototypes.
Each tool has a special job in testing PCBs. Using the right tools helps catch problems early, save money, and make reliable products. Advanced tools also keep you ahead in the fast-changing electronics world.
Comparing EMS PCB and PCB Testing
Differences in Purpose and Objectives
EMS PCB is about making and assembling circuit boards. Its main goal is turning designs into working products that follow rules. This process ensures boards are strong and ready for devices. PCB testing, however, checks if these boards work properly. It finds problems, tests performance, and ensures safety and quality standards are met.
Think of EMS PCB as the builder and PCB testing as the checker. EMS PCB makes sure the board is built right. PCB testing makes sure it works right. Both aim for great electronics, but their goals are different.
Variations in Processes and Techniques
EMS PCB and PCB testing use different steps and methods. EMS PCB includes preparing materials, placing parts, and soldering. These steps focus on accuracy and speed to match designs.
PCB testing uses methods to check how boards work and last. These include:
- Power-On Testing: Turns on the board to check basic functions.
- Manual Testing: Experts look at outputs to find issues.
- Automated Testing: Machines test performance with programmed inputs.
- Burn-In Testing: Stresses the board to find early problems.
- Margin Testing: Tests how boards handle tough conditions.
- Regression Testing: Checks if changes affect performance.
- In-Circuit Emulation: Tests parts without needing real components.
These methods show EMS PCB focuses on making, while PCB testing ensures quality.
Tools and Technologies: EMS PCB vs. PCB Testing
EMS PCB and PCB testing use different tools for their jobs. EMS PCB uses machines like pick-and-place systems and soldering tools to make boards faster. For example, Flex Ltd.’s Sketch-to-Scale® tool speeds up making products.
PCB testing uses tools to find problems and check performance. Tools like multimeters, oscilloscopes, and cameras are important. Advanced tools, like X-ray machines and heat cameras, find hidden issues and ensure boards work well.
Using these tools also saves money. Automated testing systems can cut energy use by 30%. This improves efficiency and supports eco-friendly goals, which many customers want.
Outcomes and Deliverables of Each Process
When looking at EMS PCB and PCB testing, their results show their different jobs in making electronics. Each process adds special value to create strong and high-quality circuit boards.
EMS PCB Outcomes and Deliverables
EMS PCB turns designs into real, working circuit boards. Its results focus on accuracy, speed, and flexibility. Here’s what EMS PCB provides:
- Fully Assembled PCBs: Circuit boards are made with all parts placed and soldered correctly. These boards are ready to be used in devices.
- Flexible Production Sizes: Whether you need a few boards or many, EMS PCB adjusts to your needs while keeping quality high.
- Affordable Manufacturing: By improving workflows and using bulk production, EMS PCB lowers costs without losing quality.
- Standards Compliance: Boards meet industry rules like IPC-6012B and IPC-A-600F, ensuring they are strong and reliable.
- Tracking Ability: Each board has a unique code to track its history and fix problems quickly.
Pro Tip: Working with a skilled EMS PCB provider can speed up production and help you launch products faster.
PCB Testing Outcomes and Deliverables
PCB testing makes sure the boards made by EMS PCB work as they should. Its results focus on checking quality and reliability. Here’s what PCB testing offers:
- Problem-Free Boards: Testing finds and fixes issues like bad soldering, broken circuits, or short circuits.
- Performance Checks: Boards are tested in real-world conditions to ensure they work well in their intended use.
- Safety Reports: Testing gives proof that boards meet safety and quality rules, like ISO and UL standards.
- Longer Product Life: Testing spots weak points early, helping products last longer and lowering repair costs.
- Customer Trust: Well-tested boards build confidence with buyers and improve your brand’s reputation.
Did You Know?: Advanced tests like X-rays can find hidden problems that regular checks might miss, making boards more reliable.
Comparing the Deliverables
The table below shows the main results of EMS PCB and PCB testing:
| Aspect | EMS PCB | PCB Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Main Goal | Making and assembling boards | Checking quality and functionality |
| Key Results | Finished boards, flexible production | Problem-free boards, performance checks |
| Compliance | Follows manufacturing rules | Meets safety and regulatory standards |
| Added Value | Fast and cost-effective production | Better reliability and customer trust |
Both processes work together. EMS PCB builds the boards, while PCB testing ensures they work properly.
Conclusion: Knowing the results of EMS PCB and PCB testing helps you make better choices for improving production and product quality.
How EMS PCB and PCB Testing Work Together
How Manufacturing and Testing Depend on Each Other
Making and testing PCBs go hand in hand. You need both to create high-quality boards. EMS PCB makes the boards, while PCB testing checks if they work and are safe. Together, they create a system that keeps improving.
For example, testing finds problems like bad soldering or broken circuits. This helps the manufacturing team fix issues for future batches. One factory used a chi-square test to study soldering problems. By solving the main issues, they made boards more reliable and cut repair costs.
In industries like cars and electronics, this teamwork has big benefits:
- A brake part maker lowered defects by 20% after fixing production flaws.
- An electronics company improved PCB cooling, making batteries last 20% longer.
These examples show how working together improves quality and saves time.
Pro Tip: Make sure your manufacturing and testing teams share ideas. This can help find hidden problems and improve results.
Working Together to Keep Quality High
For great results, EMS PCB and PCB testing teams must work closely. When they do, errors drop, and products become more reliable.
Testing teams can help during the design stage. They might suggest changes to make boards easier to build or stronger. During production, testing data can guide quick fixes to meet quality goals.
Two key metrics show how well this teamwork works:
- FPY (First Pass Yield): This shows how many boards pass all tests the first time. A high FPY means fewer mistakes.
- DPMO (Defects per Million Opportunities): This tracks defects per million chances. Lower numbers mean better quality.
By focusing on these numbers, you can find weak spots and improve them. This saves money and reduces waste.
Did You Know?: Companies with strong teamwork between making and testing often waste less and earn more.
Real-Life Examples of EMS and Testing Teamwork
Real-life stories show how combining EMS PCB and PCB testing can change production. Here are some examples:
| Case Study | What They Did |
|---|---|
| Big Shoe Brand | Built automated systems for shoes, adding testing steps. |
| Power Supply Company | Checked how easy custom power supplies were to make and tested them. |
| Electronics Company | Quickly made PCBs for VR/AR devices, focusing on building and testing. |
| Medical Device Project | Redesigned a device with testing at every step, from design to production. |
| Hygiene Monitoring Device | Made PCBs for hygiene tools, using automated building and testing. |
For instance, a medical device project added testing to every stage. This cut production time and made the product better.
Metrics also prove the value of this teamwork:
| Metric | What It Shows |
|---|---|
| Defects per Million Opportunities (DPMO) | Tracks defects per million chances, showing quality levels. |
| First Pass Yield (FPY) | Measures how many boards pass all tests the first time. |
| Rework Rate | Shows how many boards need fixing, with lower rates meaning better quality. |
| Scrap Rate | Tracks unusable boards, with lower rates showing better productivity. |
By following these practices, you can save money, work faster, and make better products.
Conclusion: Combining EMS PCB and PCB testing is key to making top-quality electronics. It’s not just smart—it’s necessary for success.
EMS PCB production and PCB testing have different but connected jobs. EMS PCB turns designs into working circuit boards. PCB testing checks if these boards work well and are safe. Together, they ensure electronics are reliable and high-quality.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Quality Checks | Genus Electrotech Ltd uses checks during production to keep high standards from start to finish. |
| Certifications | They earn certifications by passing strict quality audits. |
| Integrated Approach | Their integrated methods improve reliability and performance in making electronics. |
By learning these steps and working together, you can make better products, lower mistakes, and impress customers.
FAQ
What is the main difference between EMS PCB and PCB testing?
EMS PCB is about making and assembling circuit boards. PCB testing checks if these boards work well and meet quality rules. EMS PCB builds the boards, while PCB testing ensures they are reliable and perform correctly.
Why is PCB testing essential in electronics manufacturing?
PCB testing finds problems, checks safety rules, and tests performance. It stops expensive failures, makes products more reliable, and earns customer trust by ensuring high-quality electronics.
Can EMS PCB providers handle both manufacturing and testing?
Yes, many EMS PCB providers also do testing. They use tools like AOI cameras and X-ray machines to check boards during production for safety and quality.
How do EMS PCB and PCB testing improve product quality?
EMS PCB makes sure boards are built correctly and follow designs. PCB testing finds mistakes and checks if boards work. Together, they lower errors, improve reliability, and meet industry standards.
What tools are commonly used in PCB testing?
PCB testing uses tools like multimeters, oscilloscopes, flying probes, and X-ray machines. These tools find problems, test performance, and ensure boards meet safety and quality rules.
Pro Tip: Work with EMS PCB providers who include testing. This saves time and ensures great results.