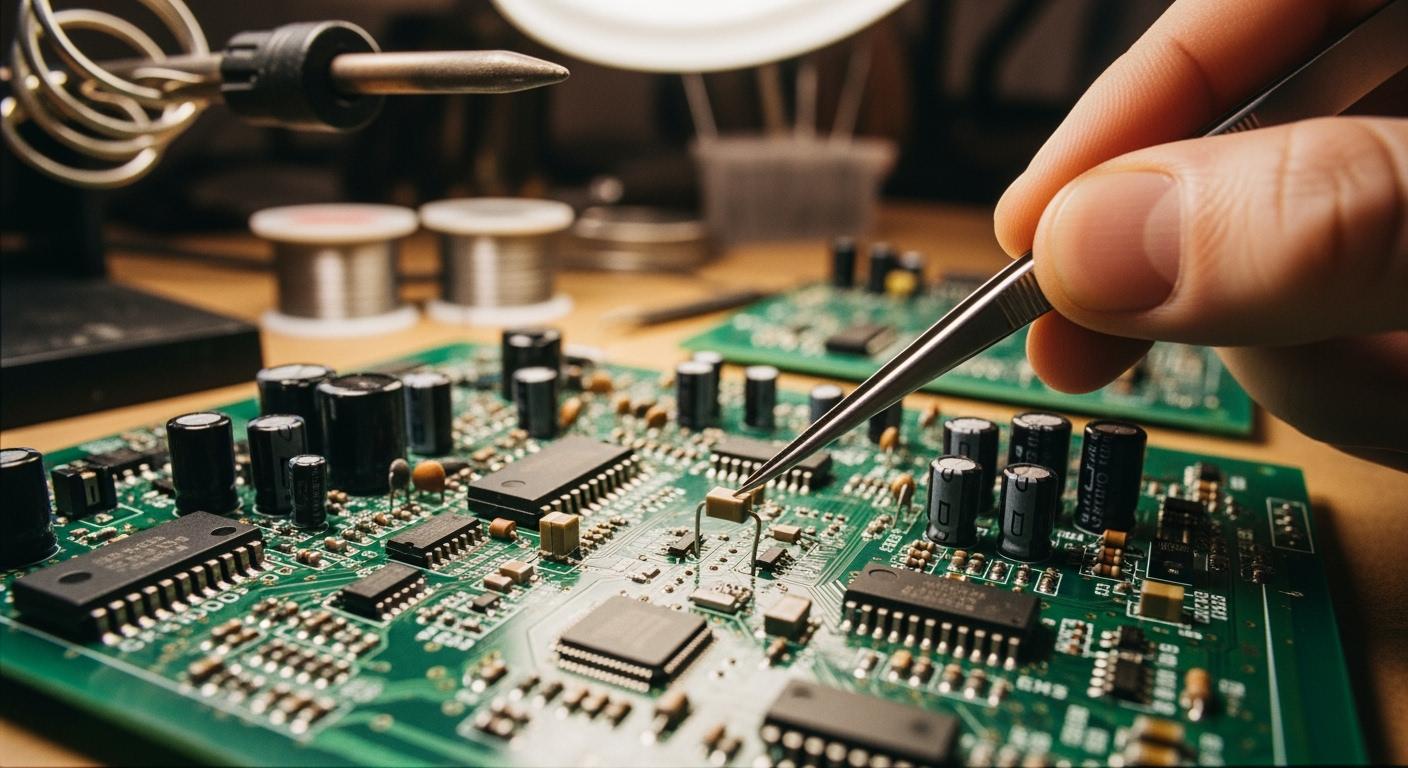
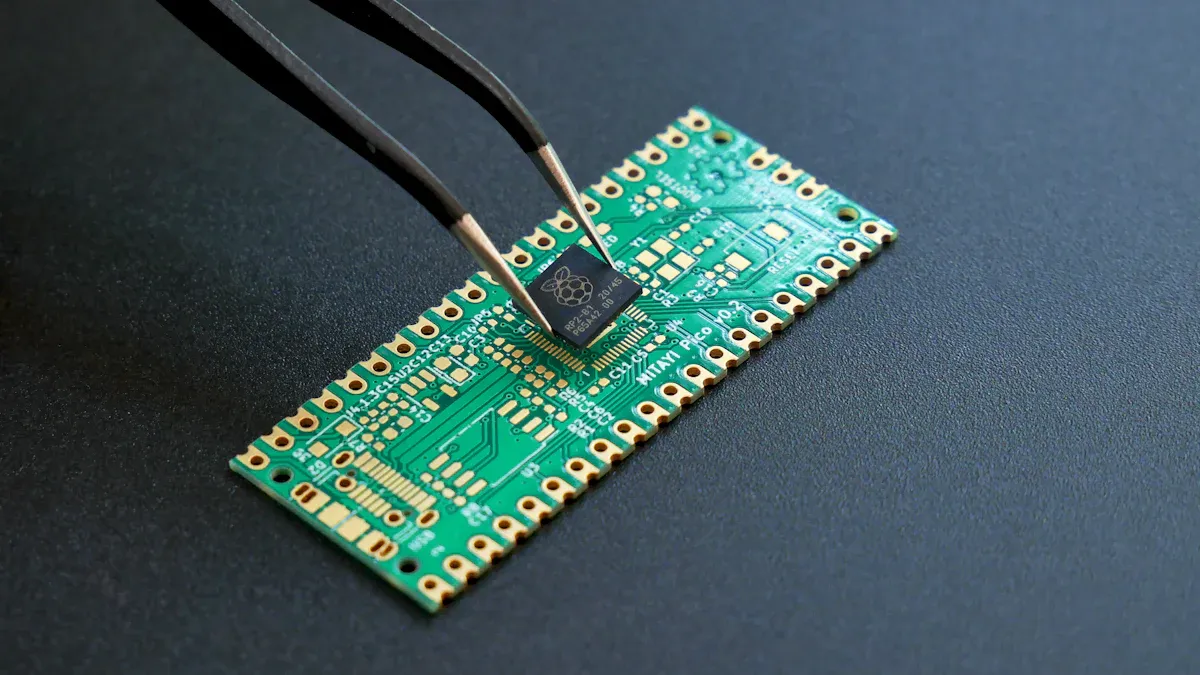
You encounter pcba every day, whether you realize it or not. A pcba is the finished board where engineers have installed and soldered electronic components onto a printed circuit board. Unlike a bare PCB, a pcba makes devices work.
PCBA powers smartphones, cars, and even medical devices.
- In 2023, the global PCB and pcba market reached $68.4 billion.
- The demand for advanced pcba grows with new technology and industries.
PCB assembly, PCBA manufacturer, OEM & ODM services help you bring ideas to life.
Key Takeaways
- PCBA is essential for modern electronics, powering devices like smartphones and medical equipment.
- Understanding the difference between PCB and PCBA helps in making informed decisions for electronics projects.
- Choosing a reliable PCBA manufacturer ensures quality control and efficient production, leading to better product outcomes.
PCBA vs PCB
What is a Printed Circuit Board?
You rely on a printed circuit board every time you use an electronic device. A printed circuit board acts as the backbone of modern electronics. It consists of a thin, insulating base—often made from materials like resin-bonded paper or fiberglass—coated with copper on one or both sides. This copper forms intricate pathways, called traces, that connect different parts of a circuit.
- Printed circuit boards provide mechanical support for electronic components.
- Copper traces on the board guide electrical signals between resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits.
- Most electronic devices, from computers to home appliances, use printed circuit boards as their foundation.
IPC standards guide the design, assembly, and inspection of printed circuit boards, ensuring quality and reliability in the electronics industry.
The construction of a printed circuit board involves several layers and materials. The table below outlines the main layers you will find in a typical board:
| Layer Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Core | A solid, nonconducting material laminated with copper, serving as the base for the PCB. |
| Copper Foil | The conductive layer where circuit designs are printed, with traces left on the PCB after etching. |
| Signal Plane | Carries electrical signals across components, designed with impedance considerations. |
| Power Plane | Distributes power supply voltages to components, providing low-impedance paths for power. |
| Ground Plane | Provides a return path for electrical currents, acting as a stable reference for voltage levels. |
| Prepreg | A dielectric material that serves as an isolation layer between conductive layers. |
| Routing Layer | Dedicated to routing electrical traces between components, sandwiched between other layers. |
You will often see materials like FR-4, a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate, or polyimide, which offers high thermal stability. The choice of material affects the performance, durability, and cost of the printed circuit board.
What is Printed Circuit Board Assembly?
A printed circuit board assembly transforms a bare printed circuit board into a working electronic device. You start with a blank board, then add and solder electronic components to create a functional circuit. This process is known as pcb assembly.
The steps in printed circuit board assembly include:
- Solder paste application: You apply solder paste to specific areas of the printed circuit board using a stencil.
- Pick and place: Robotic machines place components like resistors, capacitors, and ICs onto the board.
- Reflow soldering: The board passes through a reflow oven, where the solder paste melts and forms permanent connections.
- Inspection and quality control: You inspect the board to ensure all components are correctly placed and soldered.
- Through-hole component insertion: For some designs, you insert components with wire leads into drilled holes and solder them.
- Final inspection and functional test: The completed printed circuit board assembly undergoes testing to verify performance.
You will encounter three main types of component mounting during pcb assembly:
- Through-hole assembly: Components with leads go through holes in the board and are soldered on the opposite side. This method works well for connectors and large capacitors.
- Surface mount technology: Components mount directly onto the surface of the printed circuit board, allowing for smaller parts and higher density.
- Mixed technology assembly: Some designs use both methods on the same board for complex circuits.
A pcba manufacturer or pcba supplier manages this process, ensuring each printed circuit board assembly meets strict quality standards. Many companies offer oem & odm services, which help you design, prototype, and produce custom pcb assemblies for your unique applications.
Key Differences
You might wonder how a printed circuit board differs from a printed circuit board assembly. The table below highlights the main distinctions:
| Feature | Bare PCB | Assembled PCB (PCBA) |
|---|---|---|
| Components | Contains no components; just copper traces | All components mounted and soldered |
| Functionality | Cannot function without electronic parts | Fully functional circuit |
| Manufacturing Stage | Result of fabrication stage | Result of SMT assembly processes |
| Testing | Basic checks for continuity | Comprehensive testing like ICT |
| Cost | Significantly cheaper | Higher cost due to components and labor |
You can also compare the two using this ordered list:
- Definition: A pcb is a printed circuit board with only the base material and copper traces. A pcba, or printed circuit board assembly, includes all the mounted and soldered components, making it a complete, working circuit.
- Manufacturing process: You create a pcb by designing the layout, etching copper pathways, and drilling holes. For a pcba, you add steps like stencil printing, component placement, and soldering.
- Cost: A pcb costs less because it lacks components. A pcba includes the cost of parts, labor, and engineering, which can make up over 70% of the total expense.
Tip: When you work with a pcba manufacturer, you benefit from their expertise in pcb assembly, quality control, and oem & odm services. This partnership helps you bring your electronic ideas to life efficiently and reliably.
You need both a printed circuit board and a printed circuit board assembly to create any modern electronic device. The pcb provides the structure and connections, while the pcba delivers the functionality. By understanding these differences, you can make better decisions when choosing a pcba supplier or planning your next electronics project.
PCBA Assembly Process
PCB Assembly Steps
You begin the pcba process by designing the circuit and generating Gerber files. These files guide the manufacturing of the printed circuit board. After manufacturing, you procure electronic components and prepare them for assembly. The next step involves loading the pcb and producing a stencil for solder paste application. You apply solder paste to the board, then use pick-and-place machines to position electronic components. Soldering follows, using techniques such as reflow soldering, wave soldering, or selective soldering. You perform post-solder inspection and quality control to catch defects. Testing and debugging ensure the pcba functions as intended. You complete the process with final assembly and packaging.
Common soldering methods include hand soldering, surface mount technology, and through-hole technology. You may also use laser soldering or flip chip techniques for advanced pcba fabrication processes.
Role of PCBA Manufacturer
A pcba manufacturer guides you through every stage of manufacturing. You rely on their expertise for inspection and quality control, which includes visual inspection, automated optical inspection, and x-ray inspection. They use in-circuit testing and functional testing to verify reliability. The table below shows how pcba manufacturers ensure product quality:
| Role of Testing and Inspection | Description |
|---|---|
| Detect Defects Early | Identifying defects early minimizes costs. |
| Ensure Compliance with Specifications | Verifies that pcba meets design requirements. |
| Prevent Field Failures | Reduces risk of failures in real-world use. |
| Improve Product Quality | Leads to higher customer satisfaction. |
| Maintain Process Control | Testing data helps improve manufacturing. |
You benefit from collaboration methods such as design for manufacturability, design for testability, and bill of materials validation. These steps help you avoid supply risks and production challenges.
OEM & ODM Services
You choose between OEM and ODM services based on your needs. OEM services allow you to provide the design, while the pcba manufacturer focuses on production. ODM services let the manufacturer handle design using their expertise. The table below compares these options:
| Aspect | OEM Service | ODM Service |
|---|---|---|
| Design Responsibility | You provide the design. Manufacturer produces. | Manufacturer designs and produces. |
| Intellectual Property | You retain IP rights. | IP rights may belong to manufacturer. |
| Cost Structure | Higher upfront cost, lower per-unit cost. | Lower upfront cost, higher per-unit cost. |
| Customization Level | High customization. | Limited customization. |
You gain flexibility and scalability in pcba production. Advanced design tools and comprehensive quality management systems support your project from concept to delivery. End-to-end electronic design services help you achieve product differentiation and meet market demands.
PCBA in Electronics
Importance of PCBA
You depend on pcba for every modern electronic device. Pcba integrates multiple components onto a single board, which increases efficiency and supports complex circuit design. You see the impact of pcba in the miniaturization of devices. Pcba enables you to use compact smartphones, smartwatches, and wearables. You benefit from faster data processing and lower latency because pcba reduces the distance between components. Pcba also improves energy efficiency, which extends battery life in portable devices. You rely on pcba for enhanced product quality and performance. Pcba supports the demands of today’s electronics market by allowing manufacturers to pack over 1,000 components into a small area. You notice that pcba is essential for real-time data analysis and high-definition media. Pcba helps you achieve product differentiation and meet market expectations.
You face challenges when integrating pcba into products. You encounter sourcing difficulties, component availability issues, and higher manufacturing costs. You must address soldering defects, improper component placement, and board warping. You also manage supply chain shortages and design defects. Pcba requires careful thermal management and attention to electrical noise. You need to prevent gaps in solder joints, cold solder joints, and solder balling. Pcba demands strict quality assurance to ensure reliability. You rely on environmental stress testing, electrical stress testing, and accelerated life testing to verify reliability. Pcba helps you reduce costs by identifying failures early and ensures safety for critical applications. You achieve customer satisfaction and regulatory compliance through reliable pcba.
Common Applications
You find pcba in a wide range of applications. Pcba powers consumer electronics such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops. You use pcba in automotive systems, including engine control units and infotainment systems. Pcba supports medical devices, industrial automation, and aerospace systems. You rely on pcba for IoT sensors, smart home devices, and communication equipment. Pcba enables miniaturization, which is crucial for portable devices and wearables. You benefit from optimized space usage and enhanced functionality. Pcba drives market growth, with the global market projected to reach $92.4 billion by 2029. You see a growth rate of about 5% due to the miniaturization trend. Pcba remains the foundation for innovation and performance in electronics.
You recognize pcba as the heart of modern electronics. The table below highlights the difference between PCB and pcba.
| Aspect | PCB | pcba |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Bare board | Functional board |
| Function | Non-functional | Executes tasks |
| Manufacturing | Layering | Component placement |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Application | Prototyping | Finished products |
You make better decisions in electronics by understanding pcba.
- Efficient design
- Improved prototyping
- Enhanced reliability
- Cost-effective manufacturing
- Faster time-to-market
You see pcba as the complete solution for electronic devices. pcba powers innovation, reliability, and efficiency. pcba transforms ideas into working products. pcba supports quality control and advanced manufacturing. pcba enables rapid prototyping and market entry. pcba drives technological progress. pcba ensures product safety and compliance. pcba helps you meet industry standards. pcba is essential for every electronic device. pcba answers the question: What is pcba? It is the assembly that brings electronics to life.
FAQ
What is the difference between SMT and through-hole assembly?
You use SMT for small components on the board surface. You use through-hole for larger parts with leads that go through holes.
How do you choose a reliable PCBA manufacturer?
You check certifications, review customer feedback, and request sample boards. You confirm quality control processes and communication standards.
Can you repair a faulty PCBA?
You can repair a faulty PCBA by replacing damaged components, re-soldering connections, or using diagnostic tools to identify issues.