How Industrial PCB Assembly Works and Why It Matters

Industrial PCB assembly builds the electronic heart of machines you use. You see its work in things that run factories, hospitals, and cars. This process makes PCBs with new technology. It checks that each board follows strict rules.
- Industrial PCB assembly helps electronics grow by using new ideas.
- Many fields like cars, healthcare, and home electronics need this assembly.
- Companies work on new ideas, good quality, and being green to lead.
You count on PCB assembly for products you can trust. This process changes how modern devices work and how long they last.
Key Takeaways
- Industrial PCB assembly is very important for making strong electronics used in factories, hospitals, and cars.
- The assembly process uses careful quality checks and new technology to make sure the electronics work well and last long.
- Knowing the differences between Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Through-Hole Technology (THT) helps people pick the best way for each job.
- Using machines in PCB assembly helps work go faster, makes fewer mistakes, and makes better products, so it is very important for today’s factories.
- Following rules and quality standards keeps PCB production safe and reliable, which is good for both the people who make them and the people who use them.
What Is Industrial PCB Assembly?
Definition and Key Features
Industrial pcb assembly is how people make the main parts for machines in factories, hospitals, and cars. This assembly makes printed circuit boards that must be very strong and work well. The boards have to follow strict rules for how good they are. Industrial pcb assembly uses special materials and careful steps. These steps help each pcb work in hard places.
Tip: Industrial pcb assembly uses High-Tg FR4 materials. These materials let the pcb work in very hot places, sometimes over 135°C.
Here is a table that shows what makes industrial pcb assembly special:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| High-reliability standards | You have to follow IPC-A-610 Class rules for good quality. |
| Material requirements for heat dissipation | You use High-Tg FR4 materials to handle high heat. |
| Rigorous manufacturing processes | You do things like cutting, drilling, and testing to check quality. |
Industrial vs. Other PCB Assembly
Industrial pcb assembly is different from pcb assembly for things like phones or TVs. Industrial pcb assembly has harder designs and puts more parts on each board. You need special skills to make these boards. You also have to check the boards more because they are used in important machines.
- Consumer electronics pcb assembly tries to save money and keep things simple.
- Industrial pcb assembly needs more skill and more tests.
- Industrial pcb assembly checks the boards more to stop problems.
You can see how different places do industrial pcb assembly:
| Region | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Asia | Asia has the biggest pcb assembly companies and lots of need for electronics. |
| North America | North America has big companies that can make advanced boards. |
| Europe | Europe needs many boards for cars, especially in Germany, the UK, and France. |
Main Industrial Applications
Industrial pcb assembly is used in many areas. Here are some examples:
- Medical Devices: PCB assembly is used in tools for finding sickness, watching patients, and implants. These tools must be cleaned and work with liquids.
- Automotive Sector: PCB assembly is used in cars for parts that feel shocks, shaking, and strong electric currents.
- Aerospace Applications: PCB assembly is used in planes and satellites. These boards must work in very hot or cold places and with strong chemicals.
Industrial pcb assembly helps make printed circuit boards for things that must last and work in tough places. You need printed circuit assembly to have safe and strong machines.
PCB Assembly Process
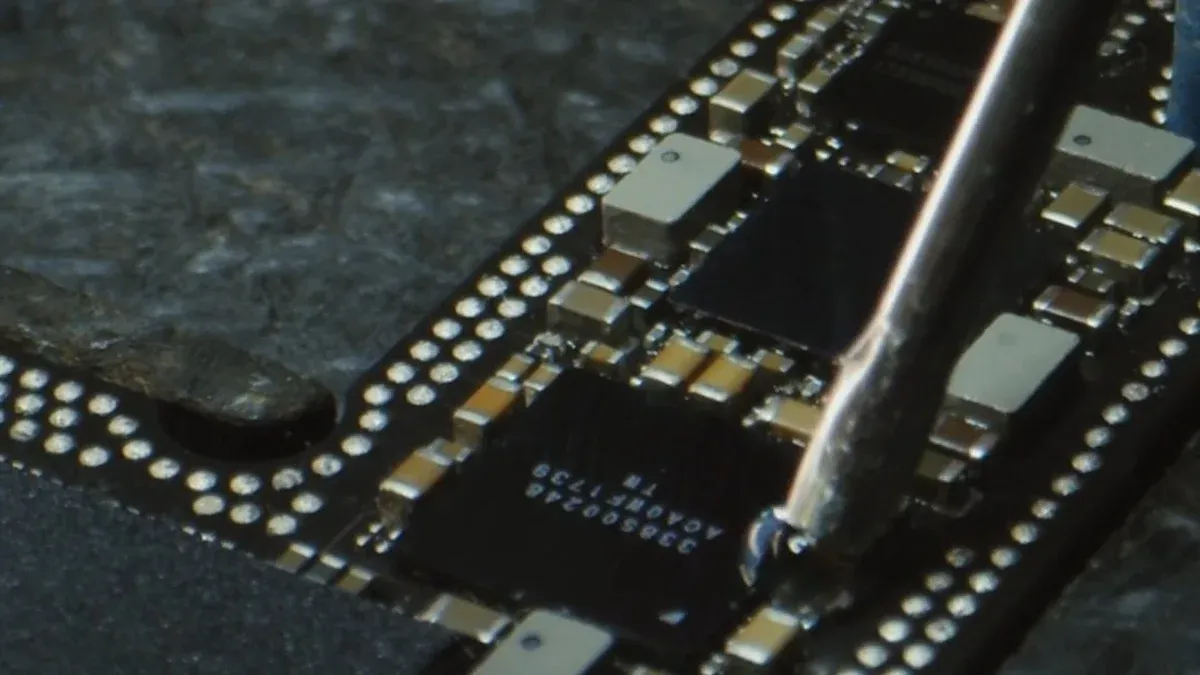
You can break down the industrial pcb assembly process into several important steps. Each step helps you build reliable and high-quality boards for machines and devices. Here is a step-by-step pcb assembly process that you will see in most factories:
- Design Verification
- Solder Paste Application
- Component Placement (SMT & Through-Hole)
- Soldering Methods
- Inspection and Quality Control
- Final Inspection and Function Test
- Cleaning, Finishing, and Shipment
Let’s look at each part of the pcb assembly process.
Design for Assembly (DFA)
You start with Design for Assembly, or DFA. This step makes sure your pcb design is easy to build and works well. When you use DFA, you make the assembly process faster and lower the chance of mistakes. You also save money and get better boards. DFA helps you:
- Simplify the assembly steps.
- Place parts in ways that make them easy to add.
- Balance what the board does with how easy it is to make.
Tip: Good DFA means you get more working boards from each batch and waste less material.
DFA gives you these benefits:
- You spend less money on making boards.
- You get your products to market faster.
- Your boards have fewer problems and last longer.
- You do not need to fix as many boards or throw them away.
Solder Paste Application
Next, you put solder paste on the pcb. Solder paste is a sticky mix of tiny metal balls and flux. It holds the parts in place before you heat the board. You use a stencil to put the paste only where you need it.
Here is a table that shows the main types of solder paste and their best uses:
| Solder Paste Type | Advantages | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Lead-Free Solder Paste | Good for the environment; strong for high-reliability boards. | Medical devices, consumer electronics. |
| No-Clean Solder Paste | Saves time and money; great for big batches. | IoT devices, mass production. |
| Water-Soluble Solder Paste | Easy to clean; perfect for boards that must be very clean. | Medical and aerospace boards. |
| Rosin Solder Paste | Works in many cases; lasts a long time. | Prototyping, small batches. |
You pick the right solder paste based on what your board needs. For example, you use water-soluble paste for medical boards that must be spotless.
Component Placement (SMT & Through-Hole)
After you add solder paste, you place the parts on the pcb. You use two main ways: Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Through-Hole Technology (THT).
- SMT uses machines to put tiny parts on the surface of the board. This way is fast and very accurate. You can place thousands of parts each hour. SMT lets you fit more parts in a small space.
- THT means you put parts with long leads through holes in the board. You often do this by hand or with special machines. THT is slower but gives a stronger hold. You use THT for parts that face a lot of shaking or stress, like in cars or planes.
Here is a table to help you see the differences:
| Feature | Surface Mount Technology (SMT) | Through-Hole Technology (THT) |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Very fast, uses machines | Slower, often by hand |
| Accuracy | High, thanks to automation | Lower, more manual |
| Part Size | Very small | Larger |
| Part Density | High (many parts per inch) | Lower |
| Strength | Not as strong | Very strong |
| Best Use | Phones, computers, IoT | Cars, aerospace, power tools |
Note: SMT is best for small, complex boards. THT is best for boards that need to handle stress.
Soldering Methods
Now you need to attach the parts to the board. You use heat to melt the solder paste and make strong connections. The main soldering methods in industrial pcb assembly are:
- Reflow Soldering: You use this for SMT parts. You heat the whole board in an oven. The solder melts and connects the parts.
- Wave Soldering: You use this for THT parts. You move the board over a wave of hot solder. The solder sticks to the leads and pads.
- Selective Soldering: You use this for special parts that cannot handle too much heat. You apply solder only where you need it.
These methods help you make sure every part is attached well. They also help you avoid problems like short circuits or weak joints.
Inspection and Testing
You must check your boards to make sure they work. Inspection and testing are key parts of the pcb assembly process. You use many ways to check the boards:
| Technique | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Finds scratches, missing parts, or wrong placement. |
| Automated Optical Inspection | Uses cameras to spot many types of problems. |
| X-ray Inspection | Looks inside the board for hidden issues. |
| In-Circuit Testing | Checks each part and its connections. |
| Flying Probe Testing | Tests boards without special tools, good for small batches. |
| Functional Testing | Makes sure the board works as it should in real life. |
You may also use special tests like Accelerated Life Testing to see how the board handles tough conditions. Boundary Scan Testing helps you check connections between chips.
Tip: Careful inspection and testing help you catch problems early. This keeps your products safe and reliable.
By following each step in the pcb assembly process, you make sure the components of a pcb assembly work together. You get strong, high-quality boards that power important machines. Checks and balances at every step help you deliver products you can trust.
Industrial PCB Assembly Technologies

Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics are used a lot in pcb assembly today. More than 70% of factories use some kind of automation. Automation helps you put tiny parts on boards very accurately. Robots work quickly and never get tired. They help you make more boards faster and with fewer errors. Here are some ways automation helps pcb assembly:
- You get the same results every time and products you can trust.
- Robots move materials well and help cut down on waste.
- You see better quality and not as many mistakes.
- Automation keeps workers safe from dangerous places.
- You can make lots of boards fast and spend less money.
- Clean rooms are easier to keep, which is important for medical and aerospace pcb assembly.
Surface Mount Technology (SMT)
Surface Mount Technology, or SMT, is very important in pcb assembly now. SMT lets you put small parts on both sides of the pcb. This way, you can make small and strong devices. Here is a table that shows why SMT is better than old ways:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Component Density | You can add more parts to the pcb, even on both sides. |
| Reduced PCB Size | Smaller parts make smaller boards, great for tiny devices. |
| Faster and More Efficient Manufacturing | Machines put parts on fast, which saves time and money. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | You spend less on parts and work over time. |
| Enhanced High-Frequency Performance | Shorter leads help the board work better at high speeds. |
Through-Hole Technology
You still use through-hole technology for some boards. This way is best when you need strong connections. You see through-hole assembly in planes, hospitals, and cars. It is also good for boards that face shaking, bumps, or high heat. Here is a table that shows when to use through-hole technology:
| Scenario/Application | Reason for Preference |
|---|---|
| Low-volume production | Works well for small batches. |
| Prototyping | Good for testing new ideas that must be strong. |
| Aerospace and medical devices | Needed for safety and high reliability. |
| Vibration and shock environments | Stays strong in hard conditions. |
| High-temperature environments | Handles heat better than other ways. |
| High current and voltage | Works well for power supplies and amplifiers. |
Advanced Inspection Systems
You need advanced inspection systems to make sure your pcb assembly is good. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) and X-ray inspection help you find problems like parts in the wrong place or bad soldering. These systems check your boards at many steps. They help you find mistakes early and keep your products safe. AOI systems can find very small errors and help more boards pass inspection. You can use these systems at different times in the assembly process to save time and money.
Tip: If you use advanced inspection systems, you always give customers high-quality pcb products.
Importance and Impact of PCB Assembly
Role in Industrial Sectors
PCB assembly is very important in many big industries. Energy, transportation, and healthcare all need strong electronics. These electronics help keep power grids and hospital machines safe. They must work all the time and not break down. If these systems stop, it can be dangerous. The table below explains why this is important:
| Evidence Description | Relevance to You |
|---|---|
| Protecting critical infrastructure is essential for national security. Many key systems, like power grids and healthcare, use complex electronics. These must be made with security in mind. | PCB assembly keeps energy, transportation, and healthcare systems reliable and safe. |
| By focusing on national security, defense needs, and following federal rules, we ensure our PCB assembly is reliable. This supports national security and strengthens our critical infrastructure. | Reliable assembly helps your country stay strong and your daily life run smoothly. |
Benefits for Reliability and Innovation
You want products that work well and last a long time. Industrial pcb assembly helps by using strict rules and new technology. This gives you better products and new ideas. Here are some main benefits:
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Adherence to quality standards | You get fewer problems and better working products. |
| Shorter lead times | You get your products faster and can change plans quickly. |
| Environmental compliance | You help the earth by following green rules. |
| Supply chain stability | You do not have to wait long for parts or products. |
| Intellectual property protection | Your ideas and designs stay safe from being stolen. |
| Customizable solutions | You can ask for special features or new ways to build things. |
| Protection from counterfeit components | You get real parts, so your products do not break. |
| Government incentives | You can get help from programs that support new technology. |
Real-World Impact
PCB assembly is used in many devices that help people. In hospitals, it powers , and ventilators. It is also in heart monitors, pacemakers, and blood pressure monitors. In factories, pcb assembly helps robots and machines work. The market for industrial pcb assembly is getting bigger. It is over the next five years. This is because more people want electronics, cars, and automation. When you use pcb assembly, you help make technology safer and smarter every day.
Quality Standards and Challenges in PCB Assembly
Key Quality Standards (IPC, ISO)
You have to follow strict rules when you do pcb assembly. These rules help you make sure each pcb works well and lasts longer. The most important rules are:
- IPC-A-610 is the main book for good quality in electronic assembly.
- ISO 9001: Focuses on how you keep quality high in your factory.
- ISO 14001: Helps you care for the environment while you build.
- UL: Checks your products to make sure they are safe.
- RoHS: Stops you from using dangerous materials in your pcb.
If you follow these rules, your boards are safer and work better.
Compliance and Regulations
You have to follow many rules when you make a pcb. These rules change how you design, pick parts, and build your boards.
| Regulation | Impact on PCB Manufacturing |
|---|---|
| RoHS | Stops you from using bad materials, so you must pick safe parts. |
| REACH | Makes you find and control chemical risks in your products. |
| UL | Checks for safety, which changes how you design and build. |
If you follow these rules, you help keep people and the earth safe. You also do not get in trouble or have to wait to ship your boards.
Common Challenges and Solutions
You face many problems when you do pcb assembly. Here are some common problems and how to fix them:
- Electrical noise can make your pcb not work right. You can fix this by making good layouts and adding ground planes.
- Harder designs can cause drilling and etching mistakes. New machines and robots help you be more exact.
- Problems with getting parts can slow you down. You can plan ahead and use more than one supplier to help.
- Soldering problems like cold joints or bridging can make boards fail. Design reviews help you find these problems early.
- Putting parts in the wrong place can waste money. Design for Manufacturing (DFM) checks help you place parts better.
- Boards can bend if you use too much heat. Careful design and even heating stop this from happening.
- New rules for the environment can be hard to follow. Using green materials and good waste plans help you follow the rules.
If you use better quality checks, you see fewer mistakes. For example, mistakes can drop from 0.9% to 0.14% with better checks.
You can fix most pcb assembly problems by following rules, using smart designs, and checking your work at every step.
You have learned that industrial pcb assembly helps make better electronics for the future. This process lets devices get smaller, work better, and use new technology.
Industrial PCBs are tested in many ways. They go through tough checks for strength and chemicals. Only the best boards are sent to factories.
If you know about pcb assembly, you can become an expert. You can also save money and make devices that people can trust.
- PCB Design Guides
- A simple guide to pcb design and assembly
FAQ
What is the main purpose of industrial PCB assembly?
You use industrial PCB assembly to build strong and reliable circuit boards. These boards power machines in factories, hospitals, and cars. You need this process to make sure your devices work safely and last a long time.
How does automation help in PCB assembly?
Automation lets you place parts quickly and accurately. Robots do the same job every time, so you get fewer mistakes. You also make more boards in less time. This helps you save money and improve quality.
Why do you need both SMT and through-hole technology?
You use SMT for small, light parts. You use through-hole for big or heavy parts that need extra strength. Both methods help you build boards that fit different needs and work in tough places.
How do you check the quality of assembled PCBs?
You use many tests to check your boards. These include visual checks, automated optical inspection, and X-ray tests. You also run functional tests to make sure each board works as it should.